Cell viability is the measure of the proportion of living cells in a population. Used to determine the number of living or dead cells in a total sample so the experiment can be optimized if required. It does not differentiate between dividing and non-dividing cells.
- Viable cells = x
- Dead cells = y
- Total cells = x+y = z
- Viable cell % = (x/z)*100
Detection: Flow cytometry, MTT, XTT assay, propidium iodide.
Cell viability: Drug screening Cell cytotoxicity: Test of chemicals
Viability assays are based on:
1) Measurement of cell membrane integrity
The membrane can get damaged by disaggregation, thawing, separation, and freezing.
-
- Dye exclusion assay
-
-
- Viable cells- Have intact membranes that do not allow the dye to pass through it
- Dead cells: Dye passes through them as they possess a ruptured membrane.
- The dye used: Trypan blue, naphthalene black, erythrosin, nigrosin green
- Drawback: Reproductively dead cells do not take up the dye as well, appear as viable.
-
-
- Dye uptake assay
- Viable cells- Uptake fluorescein diacetate and hydrolyze it to fluorescein in the membrane and emit green color.
- Dead cells: Do not uptake the dye used: Propidium iodide, Fluorescein DiAcetate(FDA).
- Dye uptake assay
-
- Chromium 51 Assay
- CR51- Used for precise and accurate measurement of cytotoxicity. It binds to the intracellular protein through A.A. The Target cell is incubated with CR51 cell followed by effector cells that recognize the Target cells and rupture the membrane. The proteins begin to leak out from the cell and the degree of protein leakage is proportional to damage.
- Enzyme Release Assay
- LDH is the enzyme used in glycolysis. The presence of LDH{ Lactate Dehydrogenase(LDH)} in the surrounding media is a death marker. It is released when the membrane is damaged. It is measured by reacting with lodonitrotetrazolium or INT( a tetrazolium salt) which gives red color formazan.
- Dye used: Tetrazolium salt
- Chromium 51 Assay
2) Based on cellular respiration
Measured by oxygen utilized or carbon dioxide released by viable cells. Equipment used: Warburg manometer
3) Radioisotope incorporation
Useful for cytotoxicity. Uses radiolabeled metabolites and substrates that can be detected Labelled nucleotide: 3H thymidine into DNA and 3H uridine into RNA Labelled phosphate: Cells labeled with 32P. The damage leads to the release of phosphate that can be measured
4) Luminescence Test
Estimate ATP levels by luminescence test.
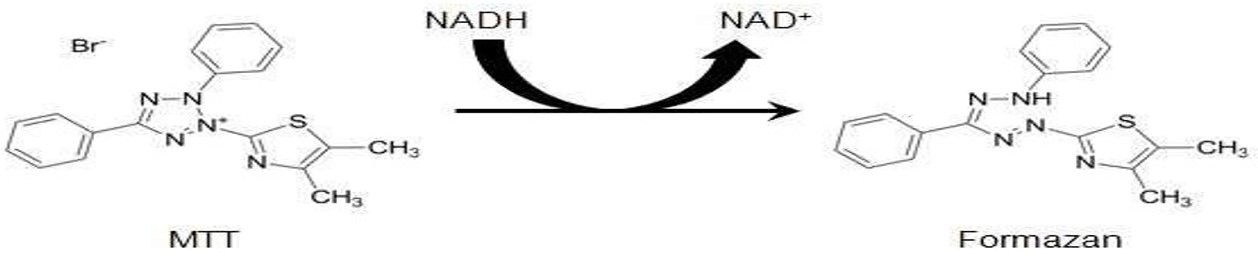
- MTT assay
- Uses general metabolism or enzymatic activity as markers of viable cells. Incubate cells to be tested with a reagent that gives luminescence that can be detected. MTT is positively charged and readily penetrates through the cell.
- Viable cells with active metabolism convert MTT to purple-colored formazan product, dead cells do give the color. Formazan accumulates as an insoluble precipitate inside the cell surface and in the medium.
-
Applications:
- Selection of tissue scaffolding for regenerative medicines
- Quality assurance for transplantation research
- Inspection of hybridoma cells