What is fasta sequence?
Fasta is a format used to represent nucleotide sequences or protein/peptide sequences. In the fasta format, the sequences are represented with their single letter code.
E.g., for nucleotides A, T, G, C, U
For proteins: A, M, D, etc.
The fasta sequence of any nucleotide or peptide begins with a single description line which is followed by the real sequence. The description line always starts with a ‘>’ sign.
The first line of a fasta tells the information about the sequence, name of the sequence.
Example:
>3SCL_1|Chains A,B|Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 chimera|Paguma larvata (9675)
STTEELAKTFLETFNYEAQELSYQSSVASWNYNTNITEENVQNMNNAGDKWSAFLKEQSTLAQTYPLQEIQNLTVKLQLQALQQNGSSVLSEDKSKRLNTILNTMSTIYSTGKVCNPDNPQECLLLEPGLNEIMANSLDYNERLWAWESWRSEVGKQLRPLYEEYVVLKNEMARANHYEDYGDYWRGDYEVNGVDGYDYSRGQLIEDVEHTFEEIKPLYEHLHAYVRAKLMNAYPSYISPIGCLPAHLLGDMWGRFWTNLYSLTVPFGQKPNIDVTDAMVDQAWDAQRIFKEAEKFFVSVGLPNMTQGFWENSMLTDPGNVQKAVCHPTAWDLGKGDFRILMCTKVTMDDFLTAHHEMGHIQYDMAYAAQPFLLRNGANEGFHEAVGEIMSLSAATPKHLKSIGLLSPDFQEDNETEINFLLKQALTIVGTLPFTYMLEKWRWMVFKGEIPKDQWMKKWWEMKREIVGVVEPVPHDETYCDPASLFHVSNDYSFIRYYTRTLYQFQFQEALCQAAKHEGPLHKCDISNSTEAGQKLFNMLRLGKSEPWTLALENVVGAKNMNVRPLLNYFEPLFTWLKDQNKNSFVGWSTDWSPYADHHHHHH
In the above fasta sequence, we can see the sequence is starting with the sign ‘>’. 3SCL is the protein data bank id of the sequence we can check further details of this sequence by searching the PDB id (https://www.rcsb.org/).
For the single letter code of amino acid click here. (X any, * translation stop, -a gap of indeterminate length)
In the fasta input blank lines are not allowed in the middle of a sequence and sequences are expected to represent in the stranded IUB/IUPAC format (amino acid and nucleic acid). Lower case letters are mapped into the upper case. If there is a gap in sequence a hyphen or dash can be used to represent that gap. Supported nucleic codes in the fasta format are:
| A: adenosine | C: cytidine | G: guanine |
| T: thymidine | N: A/G/C/T (any) | U: uridine |
| K G/T (keto) | S G/C (strong) | Y: T/C (pyrimidine) |
| M: A/C (amino) | W: A/T (weak) | R: G/A (purine) |
| B: G/T/C | D: G/A/T | H: A/C/T |
| V: G/C/A | –: a gap of indeterminate length |
The red nucleotide code treated as mismatches in the sequence at the time of alignment. If a lot of these codes in a sequence are present the query in BLAST will be rejected.
Sequence alignment
Sequence alignment is a method of arranging the DNA, RNA, or protein sequences in order. This method is used to find similarities and mismatch in sequences.
In sequence comparison after comparing two sequences the ‘:’ represents conservative sequences, ‘ ’(blank) non-conservative sequences ‘.’ Represents a semi-conservative sequence.
BLAST (basic search local alignment tool) is a tool of NCBI (National center for biotechnology information) used for sequence alignment.
Types of sequence alignment:
Local and global alignment:
In local alignment, the tool matches a portion of the input and in global alignment, the tool (Needleman-Wunsch algorithm) matches/align the sequence end to end (gaps are also considered)
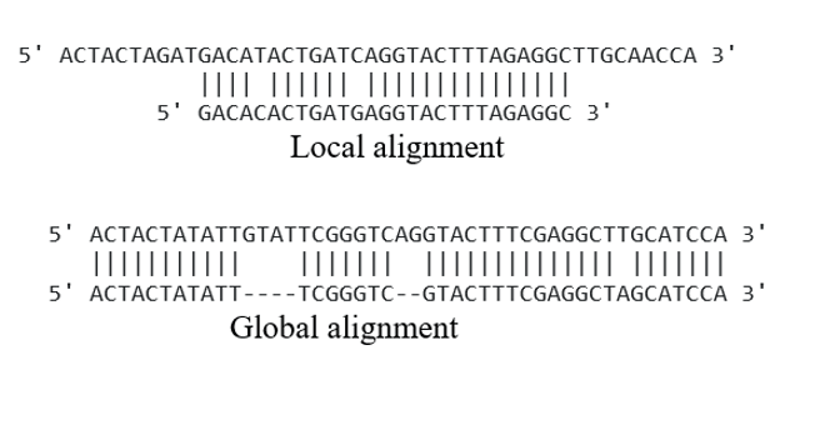
Pairwise alignment:
This method of alignment is used to find out the best fitting/matching piecewise either local or global alignment of two queries (Fasta).
References: