- The amino acid is an organic compound (Biomolecule). An amino acid contains a carboxyl group (-COOH) and an amino group (-NH2). Amino Acids are the building blocks of protein. There are 22 standard amino acids. Amino Acids are different from each other because of the attached R- group to the alpha carbon.
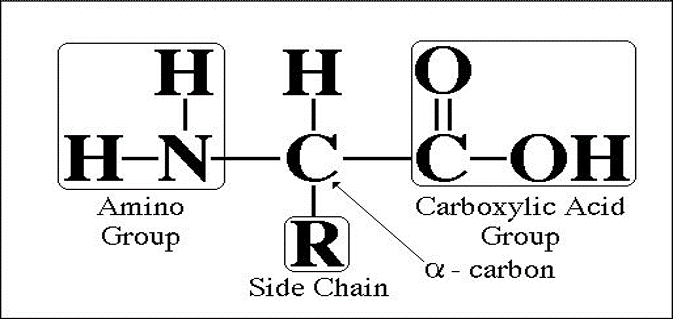
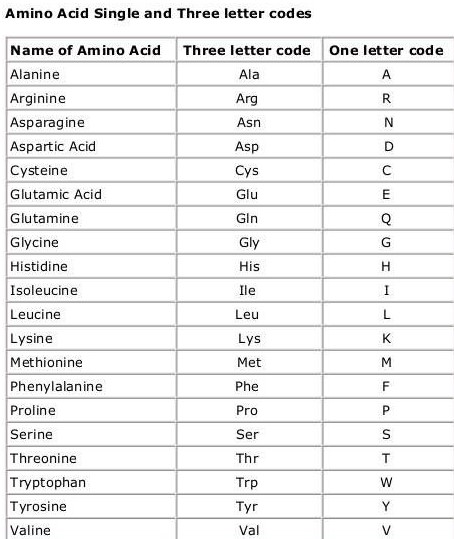
- Amino Acids form polymer chains by joining with other amino acids. Polymers are joined by a peptide bond. The translation is the process of protein making. From 22 amino acid 20, amino acids are encoded by genetic code, and the remaining two pyrrolysine and selenocysteine are incorporated by a unique synthetic mechanism. Every amino acid has a unique name and single letter code (as id)
- E.g., Glycine, Valine, proline.
- Amino Acids are classified into various categories.
- E.g., Polarity, Nutritional requirement…
- Amino acid changes into its ionic form at a specific pH known as a zwitterion.
Chemical properties of amino acids
- Amphoteric:
Amino acids have amphoteric nature (can act as acid and base both)
- Zwitterion formation:
To form a molecule with its functional groups, having a positive and negative charge.
- Ninhydrin test:
1 ml Ninhydrin on 1 ml protein solution shows violet color after heating. It shows the presence of alpha-amino acids.
- Sanger’s test:
Sanger reagent reacts with an amino group in a mild alkaline medium under cold conditions.
- Reaction with HNO3:
Reacts with the Amino group to release nitrogen and form the corresponding hydroxyl.
Classification based on polarity
- Polar Amino Acids
- Non-polar Amino Acids
- Polar amino acids:
- In this category there are 11 amino acids listed down:
- Polar Uncharged: Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine, and Tyrosine.
- Polar Charged: Histidine, Lysine, Arginine, Aspartate, and Glutamate
- Non-polar amino acid
- In this category there are 9 amino acids:
- Glycine, Alanine, Proline, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Tryptophan, Phenylalanine, and Methionine.
Essential and non-Essential amino acids
based on the requirement of our body:
- What are the Essential amino acids?
- Out of 20 amino acids, there are 9 are in the list of essential amino acids. We need to take these amino acids from outside (food sources).
- Isoleucine, Valine, Lysine, Phenylalanine, Methionine, Threonine and Tryptophan
- What are the Non-essential amino acids?
- These amino acids can be made by our body.
- Arginine, Cysteine, Glutamine, Tyrosine, Glycine, Proline, Serine, Alanine, Aspartate, and Asparagine.
What is the isoelectric point?
The pH when the total charge of an amino acid is zero, known as an isoelectric point.
Peptide bond formation
- Two molecules of amino acid joined by a peptide bond. A peptide bond is formed between the amino group and the carboxyl group. Two amino acid forms a peptide bond by releasing a water molecule. The resulting peptide is CONH (O=C-N-H)

The function of amino acids
- Building blocks of protein.
- Sustaining the health of our body.
- Structure of muscle.
- Hormone/enzyme production.
- Cellular structure
- As protein:
- For Nucleoprotein: E.g., phosphoprotein, mucoprotein,
- Protein derivatives: E.g., proteases, peptones
- Structural proteins: E.g., collagen, elastin
- Carrier proteins: E.g., channel proteins
- Transfer proteins: E.g., hemoglobin
