As we know Python is an object-oriented programming language so everything is considered as an object in Python, data types are actually classes and variables are instance (object) of these classes.
Depending upon the properties, there are manly 7 basic data types:
1. Numbers: This datatype mainly has a numerical value.
- Integer
- Float
- Complex
a = 10 print(a, "is of type:", type(a)) b = 5.0 print(b, "is of type:", type(b)) c = 1 + 2j print(c, "is of type:", type(c))
Output:

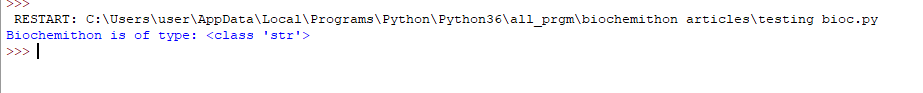
2. String: String datatype in python can be written in single or double or triple-quotes. It is sequence of characters. It is immutable data type.
string = "Biochemithon"
print(string, "is of type:",
type(string))
Output:
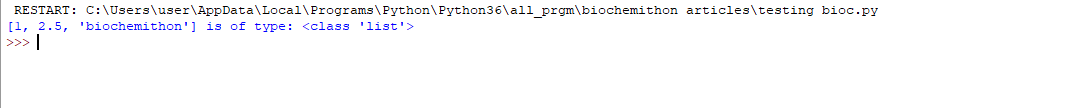
3. List: List is a collection data type which is ordered and changeable i.e. mutable.
a = [1, 2.5, 'biochemithon']
print(a, "is of type:",
type(a))
Output:
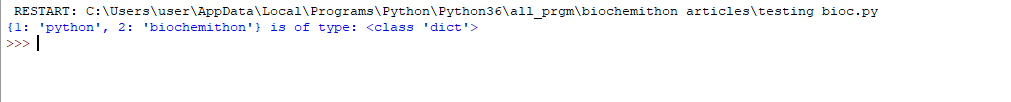
4. Dictionary: Dictionary is a collection datatype like List but it is unordered, changeable and indexed. We have key-value pairs in the dictionary. We can use keys as indexes since they are unique but the value in the key can be duplicated. Mutable data type elements can’t be used as a keys in the dictionary.
a = {1: "python", 2: "biochemithon"}
print(a, "is of type:",
type(a))
Output:
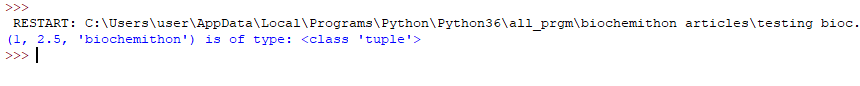
5. Tuple: Tuple is a collection datatype which is ordered and unchangeable i.e. immutable.
a = (1, 2.5, 'biochemithon')
print(a, "is of type:",
type(a))
Output:
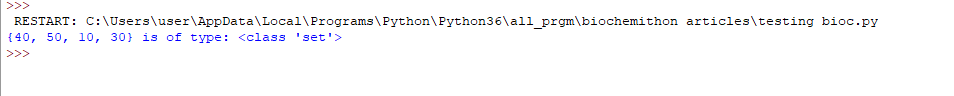
6. Set: Set is also a collection datatype but it is unordered and does not contain any duplicate values. It is mutable data type.
a = {50, 40, 30, 30, 10}
print(a, "is of type:",
type(a))
Output:
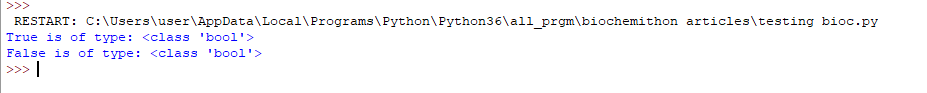
7. Boolean: This data type is either True or False. Boolean variables are defined by the True as well as False keywords. It is a immutable data type.
a = True
b = False
print(a, "is of type:",
type(a))
print(b, "is of type:",
type(b))
Output: