- Every living organism except viruses has a Cellular organization.
- Organisms having only a single cell are known as unicellular organisms example bacteria, protozoa.
- Organisms having multiple cells in their body are known as multicellular organisms.
Cells are of two types:
- Prokaryotic cells
- Eukaryotic cells
The term prokaryote and eukaryote suggested in the 1960s by Hans Ris.
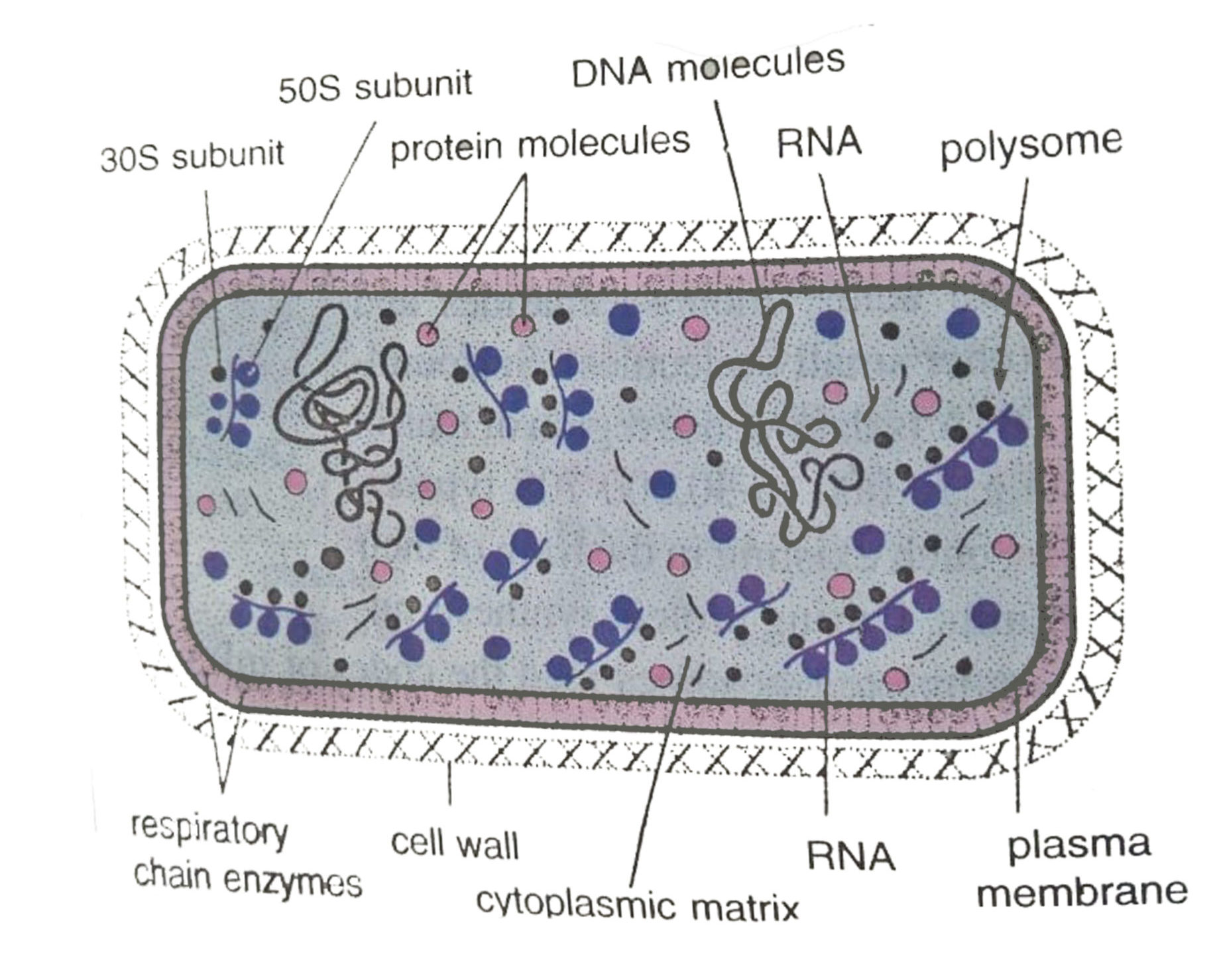
Prokaryotic cells
in Gr., pro= primitive and karyon = nucleus
- prokaryotic cells are small, simple, and most primitive cells.
- Perhaps3.5 billion-year ago stromatolites are the first cells that came into existence.
- A prokaryotic cell is a one envelope system, it consists of nuclear components that are surrounded by a cytoplasmic ground substance with the enveloped plasma membrane.
- None of the cellular components of a prokaryotic cell are very well developed and enclosed by a membrane.
- A Prokaryotic cell didn’t contain nucleoli, microfilaments, microtubules (cytoskeleton), centrioles, and basal bodies.
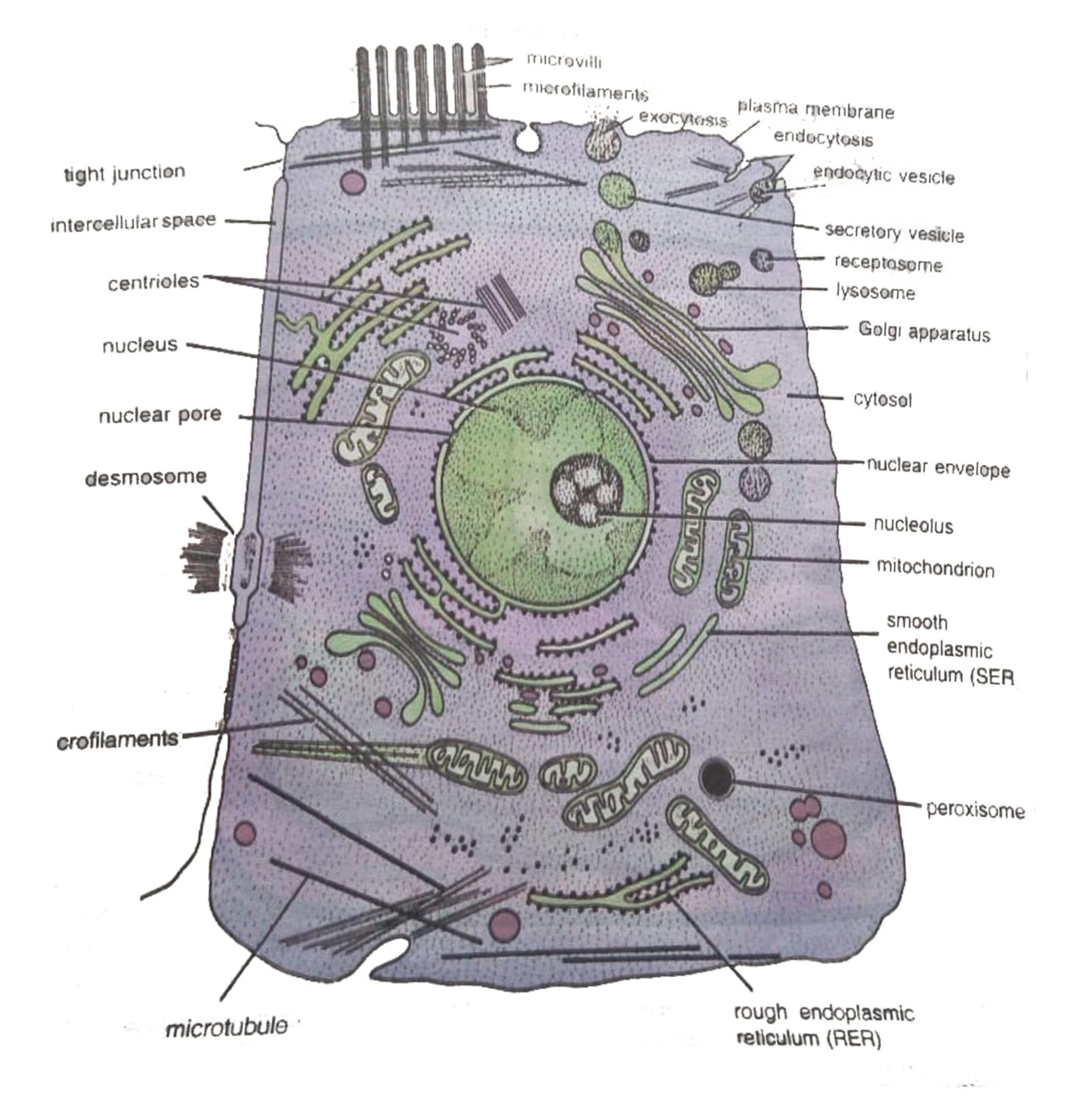
Eukaryotic cells
In Gr., eu =good, karyotic = nucleated
- eukaryotic cells are two envelop system and very much larger than prokaryotic cells.
- The primary membrane protects the cell and secondary membranes envelop the nucleus and other internal cellular organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells are the true cells which occur in plant and animal cells with different shapes, size, and physiology.
- Eukaryotic cells have a Plasma Membrane, Cytoplasm, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Golgi Apparatus, etc.
- Eukaryotic cells contain well developed cellular components and nucleus in which the genetic information is stored (DNA, RNA).
Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes:
| Features | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
| DNA | Prokaryotes have circular DNA that is naked. No introns are present | Eukaryotes have linear DNA that is bound to protein. Introns are present |
| Organelles | The nucleus is absent, cell organelles are not very well developed, no membrane is bounded
70S ribosomes are present |
Contains a nucleus, cell organelles are very well developed, and membrane-bounded, 80S ribosome are present
|
| Reproduction | Reproduction by binary fusion,
Contains single chromosome(haploid) |
Reproduction is complex (meiosis and mitosis)
Chromosomes are paired(diploid) |
| Cell size | Usually 0.5-10 µm | Usually 10-100 µm |
| Nucleoplasm | Absent | Present |
| Cell wall | Made of peptidoglycan | In plants cell wall is made up of cellulose |
| Flagella | Simple type, lack microtubules | Complex, consist of multiple microtubules |
| Ribosomes | Smaller 70S | Large 80S |
| Mucilaginous capsule | Present | Absent |
| Plasma membrane with steroid | Usually absent | Present |
| Chromatin with histone | Absent | Present |
| Plasmid | Commonly present | Rare |
| Cellular organelles
i. Mitochondria ii. ER iii. Vacuoles iv. Lysosomes v. Chloroplast vi. Centrioles vii. Microtubules |
Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent Absent |
Present Present Present Present Present (in plants) Present present |
| Example | Bacteria | Animal and plant |
Difference between animal and plant cell
| Animal cell | Plant cell |
| Cells are small | Cells are Larger than animal cells |
| The cell wall is absent | The cell wall is present and made of cellulose |
| Plastids are absent (except Euglena) | Plastids are present |
| Vacuoles are small | Large central sap vacuole |
| Highly complex Golgi apparatus | Simple units of Golgi apparatus known as Dictyosomes |
| Centrioles and centrosome are present | Lack of centrosome and centriole |
| Chloroplast is absent | Chloroplast is present |
| Lysosomes are present | Absent lysosomes |
| Reserve food as glycogen | Reserve food as starch |