Cells of Lymphoid lineage include T, B, and NK(natural killer) cells, and among these B and T cells are the part of Adaptive immune response while NK cells are the part of innate immune responses. These cells(B and T) contains a large nucleus and a thin layer of cytoplasm.
B cells
B cells also are known as B lymphocyte. These cells are the type of leucocytes. B cells have B Cell receptors on its surface which can bind to a specific antigen and adaptive response is generated against the antigen. B cell receptors are membrane-bound immunoglobulin. Once the antigen is bound to BCR, B cells differentiate into the plasma cell and the memory cell. Plasma cell secretes soluble immunoglobins.
Every B cell posses approximately 105 BCR on the plasma membrane. Each of the B cells produces a single type of antibody, each one of them having a unique antigen-binding site.
Plasma cells
Plasma cells are highly specialized for the secretion of antibodies. A single Plasma cell is capable of secreting hundreds and thousand of antibodies per second. Plasma cells do not divide and have a life span of 1-2 weeks. Plasma cells have large ER (endoplasmic reticulum) and GC (Golgi complex) these cells are only activated once B cell differentiated into plasma cells and this allows plasma cells to produce antibodies for specific antigens. These cells respond to the signals coming from T cells during an attack to pathogen and then continue to produce antibodies.
Memory B cells
The other type of cell in which B cells differentiate into is Memory B cells. These cells have a long life and these cells allow the body to respond rapidly in case of a re-exposed infection.
T cells
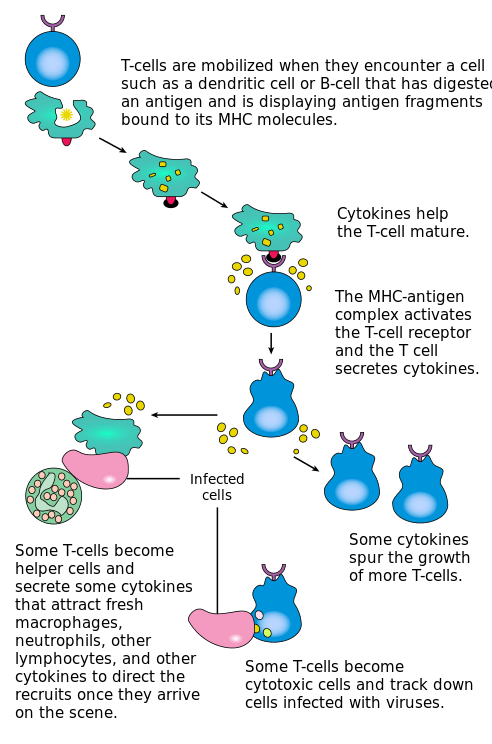
T cell is a type of leucocyte and known as T lymphocytes. T cells are originated from Bone marrow and become mature in the Thymus. T cells differentiated and multiply into cytotoxic T cells, and helper T cells. In B cells BCR is present and in the case of T cells TCR is present which is T cell receptor
T cell receptor only recognizes antigens that are bound to the cell membrane proteins known as ad MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex). MHC molecules are classified into two classes.
- MHC I (present on all nucleated cells)
- MHC II (present on Antigen-presenting cells such as Macrophage, Dendritic cells, and B Cells).
-
1. Helper T cells
- Helper T cell receptor binds to the class II MHC molecule, which is accompanied by a glycoprotein called CD4.
- Helper T cells release cytokines. The main functions of the helper T cell to help other cells to activate other cells of the immune system. That’s why they are known as T helper cells. T helper cells are further classified into 5 types:
- TH1 regulates the immune response to intracellular pathogens.
- TH2 regulates the response to many extracellular pathogens.
- TH17 secrete IL17, play important role in cell-mediated immunity, and possibly helps in the defense mechanism against fungi.
- TFH T follicular, have an important role in humoral immunity and regulates B-cell development in germinal centers.
- TREG regulatory T cells a unique capacity to inhibit an immune response in the case of autoimmune disorders.
-
2. cytotoxic T Cells
- Cytotoxic T cell receptor binds to the class I MHC molecule, which must be accompanied by a glycoprotein called CD8, which binds to the constant portion of the class I MHC molecule. CD8 are proteins expressed by T lymphocytes.
- cytotoxic t cells release the cytotoxins perforin, granzymes, and granulysin. These cytotoxins trigger the caspase and cascade, which eventually leads to program cell death/apoptosis.
- The ratio of CD4 and CD8 cells is approx. 2:1. Any change in this ratio often indicates the immunodeficiency disease, autoimmune disease, and disorders.
- References
- 1. Kuby Immunology by Thomas J. Kindt, Barbara A. Osborne, Richard Goldsby.
- 2. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 13th Edition by Madigan, Martinko, Bender, Buckley, Stahl.