In previous articles, we have already discussed innate and adaptive immunity. If you have not read those articles, click here to read
As we know cells forms tissue, tissue forms organs, and organs form a system. In this article, we have divided the cells and organs of the immune system into two categories.
- 1. Primary lymphoid Organs
- 2. Secondary lymphoid Organs
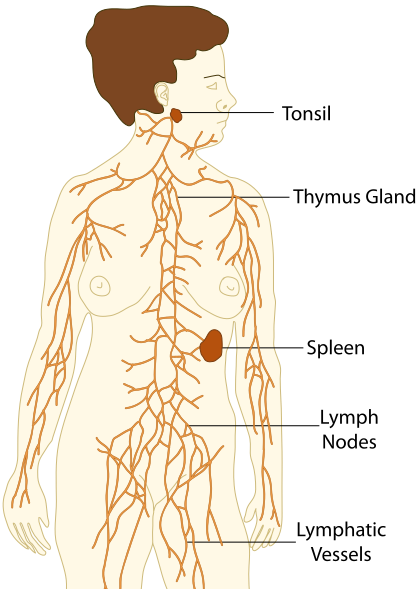
-
1. Primary lymphoid Organs
Known as the primary lymphoid organ because the formation of blood cells takes place from here. Bone marrow and thymus are counted as part of the primary lymphoid organs.
-
i. Bone marrow:
Bone marrow is a spongy tissue inside the bones including the hip and thigh bone. Bone marrow contains the immature cells known as stem cells and produces around 200 billion new RBC every day along with WBC and platelets. Bone marrow contains mesenchymal and hematopoietic stem cells. Bone marrow can be classified into two categories:
- a. Red Bone marrow: forms blood
- b. Yellow Bone marrow: produces fat, cartilage, and bones
-
ii. Thymus:
this is the site for T cell maturation and development and is located and situated above the heart or sternum. This is an irregular shaped gland which is divided into 2 main parts/lobes:
- Right lobe
- Left lobe
-
2. Secondary lymphoid Organs:
This is an arranged series of filters monitoring the contents of extracellular fluids. E.g. lymph nodes, Spleen, MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues), mucosal cells.
-
i. Lymph nodes:
These are the highly organized lymphoid organs that are located at the point of convergence of vessels of the lymphatic system. Lymph nodes collect the Extracellular fluid from tissue and return it to blood. This extracellular fluid is produced continuously by filtration from the blood and is called the lymph.
- Lymphatic system: is a part of the vascular system and an important part of the immune system. The lymphatic system contains a large network of lymphatic vessels that carries clear fluid known as lymph (Latin word lympha: water) towards the heart.
- The lymphatic system was 1st described by the Olaus Rudbeck and Thomas Bartholin in the 17th century.
-
ii. Spleen:
situated at the left of the stomach on the upper far left of the abdomen. the main word of the spleen to filter the blood such as old RBC. Old RBC’s are recycled in the spleen. Spleen is surrounded by a capsule that forms a compartmentalized structure and is divided into two categories.
- Red Pulp and White Pulp: Red pulp consists of macrophages dendritic cells and this is the site where old and defective RBCs are destroyed, and white pulp forms a Periarteriolar lymphoid sheath (PALS).
- iii. Mucosal cells: mucosal cells are the specialized epithelial cells of mucosal-associated lymphatic tissue. Mucosal cells transport the antigen from the lumen to the immune cells.