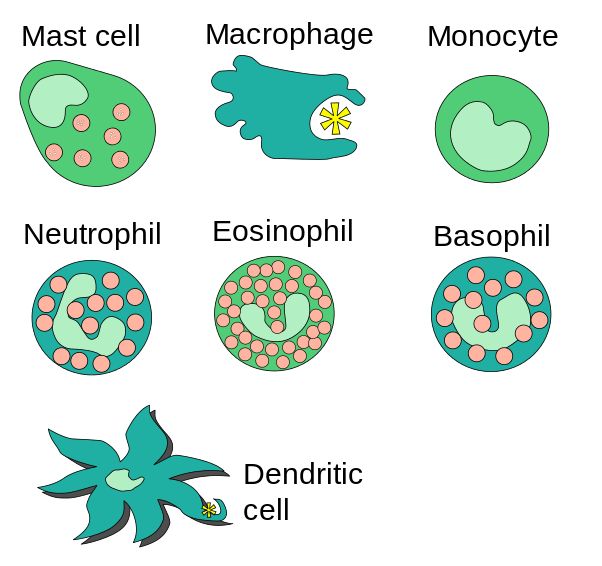
In the last article ‘Hematopoiesis’, we heard the term myeloid lineage/progenitor. These Cells (cells of myeloid lineage) are the first responder to infections. These cells include: Neutrophil, Basophil, Dendritic Cell, Monocytes and these are the parts of innate immunity.
Granulocytes
Granulocytes are known as PMN(polymorphonuclear leukocytes). Basophil, Neutrophil, and Eosinophils are categorized under granulocytes. These cells have a short life-span that contains the enzyme-rich lysosomes. Lysosome helps in the destruction of infectious microorganisms.
Neutrophils
Neutrophils are the type of granulocytes. These cells are involved in phagocytosis. Neutrophils make almost 60% of the leucocytes. Neutrophils contain a 3-5 lobbed nucleus. These are the smallest granulocytes. The dead neutrophils are the cellular components of pus.
Eosinophils
Eosinophils are characterized by a bilobed nucleus having a short life span of a few days or a week. Like neutrophils, eosinophils have phagocytic functions. Eosinophils are better appreciated as contributors to asthma and allergy symptoms and parasitic infections.
Basophils
Discovered by Paul Ehrlich. These are non-phagocytic cells. basophils have a bi-lobed nucleus. Basophils have an important role in parasitic infections and allergies. Basophil release histamine which increases blood vessel permeability and smooth muscle activity. Basophils are rare in circulation in leucocytes. Basophils are less than 1%.
Mast cells
Mast cells are found in mucous membranes and connective tissues and released from the bone marrow into the blood as undifferentiated cells. Mast cells also release histamine.
Myeloid antigen-presenting cells (APC)
Myeloid antigen-presenting cells are considered as cellular bridges between innate and adaptive immunity and are of three types.
- 1. Monocytes/Macrophages
- 2. Dendritic cells
- 3. B cells (B cells are not the part of myeloid lineage these are the part of lymphoid lineage, but B cells are categorized as antigen-presenting cells)
Monocytes
Monocytes are the agranulocytes and make 5-10% of WBC. Monocytes have an important role in opsonization. Monocytes are the largest leucocytes. These cells migrate into tissues in response to infections there it can differentiate into specific tissues macrophages. Macrophages are the phagocytic cells. Macrophages are known as:
- kupffer cells: in the liver.
- Alveolar macrophages: in the lung.
- Splenic macrophages: in the red pulp.
- peritoneal macrophages: free-floating in peritoneal fluid.
- Microglial cells: in the central nervous tissue.
Dendritic cells
Dendritic cells arise from both myeloid and lymphoid lineages of hematopoietic cells. The main function of these cells to process antigen and present it on its own surface (acts as messenger).
References
- 1. Kuby Immunology by Thomas J. Kindt, Barbara A. Osborne, Richard Goldsby.
- 2. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 13th Edition by Madigan, Martinko, Bender, Buckley, Stahl.