GENETICS
Field of biology in which we study about Heredity, genes, genetic variations in organisms. The process of Passing genes from parents to children is known as heredity. Every child inherits genes from both biological parents.
Genetic terminology:
- Trait any characteristic which can be passed from parent to progeny are known as traits.
- Heredity passing of traits from parents to progeny.
- Genetics study of heredity and genes.
- Alleles set of genes (dominant and recessive).
- Dominant stronger genes that are expressed.
- Codominance when both the alleles are dominant. Both alleles are expressed equally.
- Red flower(RR) X white flower (WW) = pink flower (RW)
- Recessive genes that show up less, responsible for the expression of the recessive characters.
- Genotype combination of genes for a trait. (WW, Ww, ww)
- Gamete cells that can reproduce (ovum, sperm), have a haploid number(23) of chromosomes.
- Phenotype physical feature from a genotype.
- Homozygous(Pure) Combination s genotype which includes 2(same) dominant or recessive genes. (WW, ww)
- Heterozygous(Hybrid) Combination s genotype which includes 1 dominant and one recessive gene. (Ww, wW)
- Chromosomes (Protein + DNA) thread-like structures are located inside the nucleus.
- Sex chromosomes determine the sex of organisms. In humans XX for females and XY for males.
- Carrier a heterozygous individual. Capable of Passing on a genetic mutation.
- Clone genetically identical copies of parents
- Mutation changes/alteration in gene
- Cross mating of two parents
- Monohybrid cross: Cross which involves only a single trait.
- Dihybrid cross: Cross that involves two traits.
- Backcross: the cross of a hybrid with one of its parents.
- Testcross: the cross of F1 progeny with the recessive parent.
Gregor Johann Mendel and Mendelian inheritance
Gregor Johann Mendel is known as the father of genetics. He gave the laws of governing inheritance of traits. He studies the inheritance traits in pea plants (Pisum sativum)
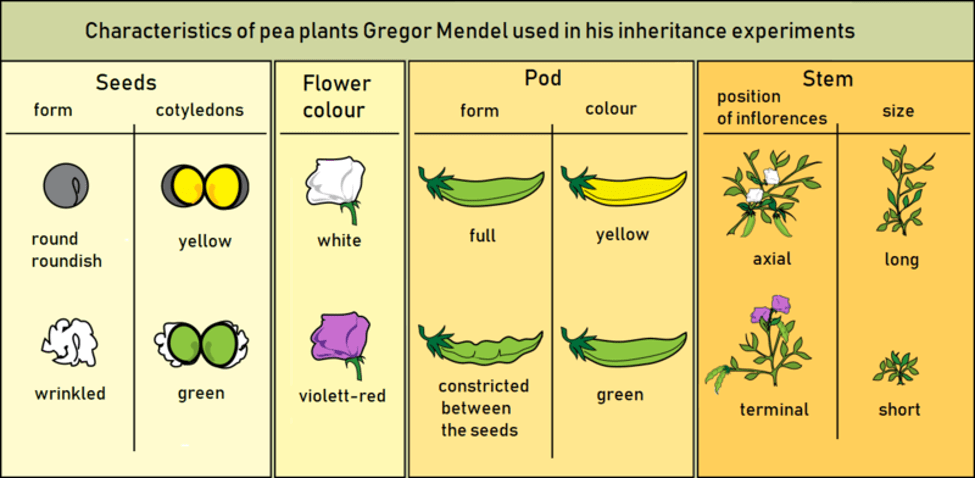
- Why Mendel chooses Pea plant?
- The reasons for choosing Pea plant for his experiment are:
- 1) Variation in the plant
- 2) Reproduction (Fertile hybrids)
- 3) Self-pollination
- 4) Short life cycle
- 5) Easy maintenance
- 6) A large number of offspring’s
Mendel’s laws are stated as:
- The law of segregation: during the formation of gametes alleles for each gene, segregate from each other so each gamete carries only one allele for each gene.
- The Law of Independent Assortment: genes of different traits can segregate independently during the process of gametes formation.
- The Law of Dominance: some alleles are dominant while others are recessive. An organism having at least one dominant allele will show the effect of the dominant allele.
References:
- Elston, R. C., Satagopan, J. M., & Sun, S. (2012). Genetic terminology. In Statistical Human Genetics(pp. 1-9). Humana Press.
- Verma, P. S. (1974). Cell biology, genetics Molecular Biology, Evolution, and ecology. Chand.