- Glycolysis is a process of conversion of glucose into pyruvate by a series of intermediate metabolites.
- Glycolysis is a part of cellular respiration
- Each chemical modification is performed by a different enzyme.
- In this process, ATP is formed in the cytoplasm.
- ATP = energy.
Steps of the process
Step 1:
- Phosphate is transferred from ATP to glucose, making Glucose-6-phosphate.
- Glucose-6-phosphate is more reactive than glucose.
- Reaction completed by the enzyme Hexokinase.
Step 2:
- Glucose-6-phosphate is converted into its isomeric form (fructose 6-phosphate).
- The reaction is carried out by glucose-6-phosphate isomerase.
Step 3:
- A phosphate group from ATP is transferred to fructose 1,6-biphosphate
- The reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase.
Step 4:
- Fructose 1,6-biphosphate splits to form two molecules, three-carbon sugar.
DHCP and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
- Both are isomers of each other.
- The reaction is completed by aldolase
Step 5:
- DHCP and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate are interconvertible.
- The enzyme used in the reaction: triose isomerase
Step 6:
- Molecules from reaction 5 one molecule get converted to 1-3, diphosphoglyceric acid
- The reaction is carried out by Phosphoglyceric dehydrogenase.
Step 7:
- 1-3, diphosphoglyceric acid is converted to 3 Phosphoglyceric acid.
- The reaction is completed by the enzyme 3-phosphoglyceric 1-kinase.
- in-between reaction 6-7 2 molecules of ADP gets converted into 2ATP.
Step 8:
- 3-phosphoglyceric acid is converted to 2-phosphoglyceric acid.
- The used enzyme in the reaction is phosphoglyceromutase.
Step 9:
- 2-phopshoglyceric acid is converted into phospho-enol pyruvate.
- By the enzyme Enolase.
Step 10:
- PEP (phospho-enol-pyruvate) gets converted to pyruvic acid.
- By the enzyme pyruvic kinase.
- 2ADP —> 2ATP
Structure of ATP
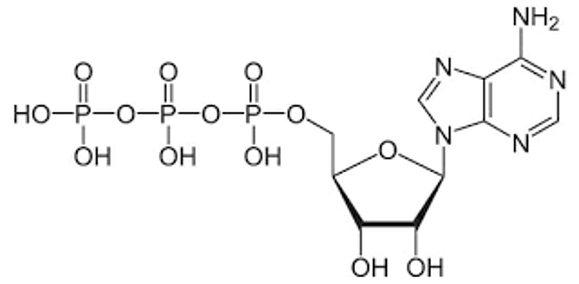
- ATP is the Adenosine triphosphate.
- It contains an adenosine base.
- A pentose-sugar.
- And 3 molecule of phosphate (alpha, beta, and gamma phosphate groups).
- A molecule of ATP provides us chemical energy.
- Energy stored in bonds
- When a molecule of ATP is breaking down it produce ADP and energy
QUESTION:
- ATP is nucleotide or nucleoside?
- Which bond in ATP stores energy?
- The amount of energy released.?
- Structure of NAD and NADH?
Function of NAD
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NAD is a coenzyme.
- Can be found in all the living cells.
- NAD is a dinucleotide.
- It consists of two nucleotides which are joined by phosphate groups present.
- Out of two nucleotides, one nucleotide has an adenine base, and the other one having nicotinamide.
- NAD exists in two forms,
- An oxidized and reduced form (NAD+)
- In metabolism NAD involved in a redox reaction.
- Carries an electron from one reaction to another reaction.
- That’s why it’s found in two forms, NAD+ is an oxidizing agent it accepts electron and became reduced.
- The transfer of electron is a main function of NAD.
- NAD acts as cofactor in redox reactions.
- Roles are involved in: Energy metabolism, mitochondrial functions.
- Having a deficiency can cause:
Deacceleration of glycolysis and Krebs’s cycle
Function od NADP
- Nicotinamide Adenine Diphosphate
- NADH plays an important role in metabolism.
- NADPH is a reduced form of NADP
- It differs from NAD by the presence of an additional PO4–
- NADP(H) provides reducing Equivalents for biosynthetic reactions.
- Oxidation-reduction involved in protecting against the toxicity of reactive oxygen species.
- As a Co-Enzyme in anabolic reaction
- As a regenerator of reduced glutathione.
- The deficiency of NAPD can lead to higher sensibility to oxidative damage.
Totally and an highly interesting post to read on this nice website. Almost never write any feedback but now i just did not resist
I just came across this blog I was I am getting a 404 page not found when trying to access other posts I hope it gets fixed. Thanks
Really liked the post you posted . it just isnt that easy to discover even remotely good posts toactually read (you know.. really READ and not simply browsing through it like a zombie before going to yet another post to just ignore), so cheers man for not wasting my time on the god forsaken internet.
Took me time to read all the feedback, however I really loved the article. It proved to be very useful to me and I am positive to all the commenters here! It is always good when you cannot only learn, but additionally engaged! I am certain you had pleasure writing this article. Anyway, in my language, there usually are not much good source like this.
My sister saved this web publication for me and I have been reading through it for the past couple hrs. This is really going to aid me and my friends for our class project. By the way, I like the way you write.
I like when you talk about this type of stuff in your blog. Perhaps could you continue to do this?