Polymerase chain reaction or PCR is developed by Karry Mullis in 1984. This is a method for the amplification of DNA. PCR is based on the capability of DNA polymerase that can synthesize a new strand of DNA that is complementary to the other strand. It is because DNA polymerase can only add nucleotide onto a preexisting 3’-OH group.
Components of PCR
DNA template:
In the process of PCR, the target sequence (which we need to amplify by the PCR) which is known as a template strand.
DNA polymerase:
DNA Polymerase is a type of enzyme that used to synthesize DNA from other dNTP’s (the building block of DNA). DNA polymerase starts the synthesis of a new strand from the end of the primer (3’OH).
The Taq DNA is the first and most common DNA polymerase to be used and obtained from Thermus aquaticus. The other polymerase used in PCR is PfuDNA polymerase, and this is obtained from Pyrococcus furiosus. PfuDNA polymerase has higher fidelity (higher accuracy of adding complementary nucleotides), the presence of Mg++ ions in the buffer solution acts as co-factor for DNA polymerase.
Primers:
Primers are synthetic DNA strand of small nucleotides sequences which are complementary to 3’ end of the template strand. There are two primers used in the method of PCR (forward and reverse primer).
Nucleotides (dNTP ‘s or deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate):
All nucleotides are the building blocks for new DNA strands and essential for reaction in the process of PCR. It includes the nucleotides bases, adenine (A), Guanine(G), cytosine(C), Thymine(T), Uracil (U) uracil is present in RNA.
Procedure:
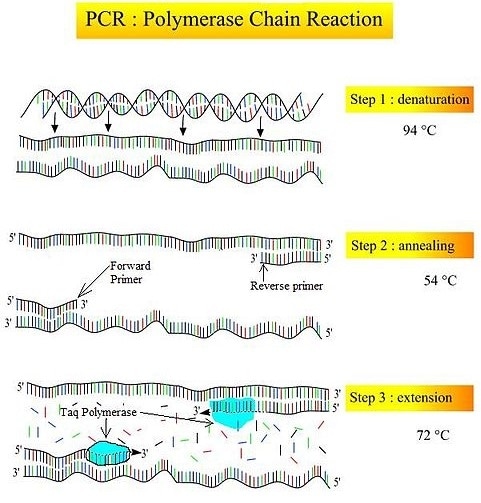
Denaturation:
The first step is Denaturation. In this step, the DNA is heated up to 94 °C for at least 1 min. and this causes the separation of the DNA double helix. After separation, each on the DNA strand acts as a template strand for the synthesis of the complementary strand.
Annealing:
The required temperature for this process is 55-65 °C. in this step the temperature is cooled down because the primers need to be bind to their complementary sequences.
Extension:
the temperature required in this process is 72 °C. In this step, the temperature is again raised so the Taq polymerase can work properly and extend the primers to help in the synthesis of a new strand of DNA.
Final hold:
The first three steps are repeated 35-45 times and produce millions of exact copies of the target DNA. The process can take 2-4 hours and it also depends on the length of the DNA to be copied.
Applications of PCR
- Diagnosis of bacterial diseases.
- Genetic fingerprinting.
- To find out genetic diseases.
- Gene sequencing